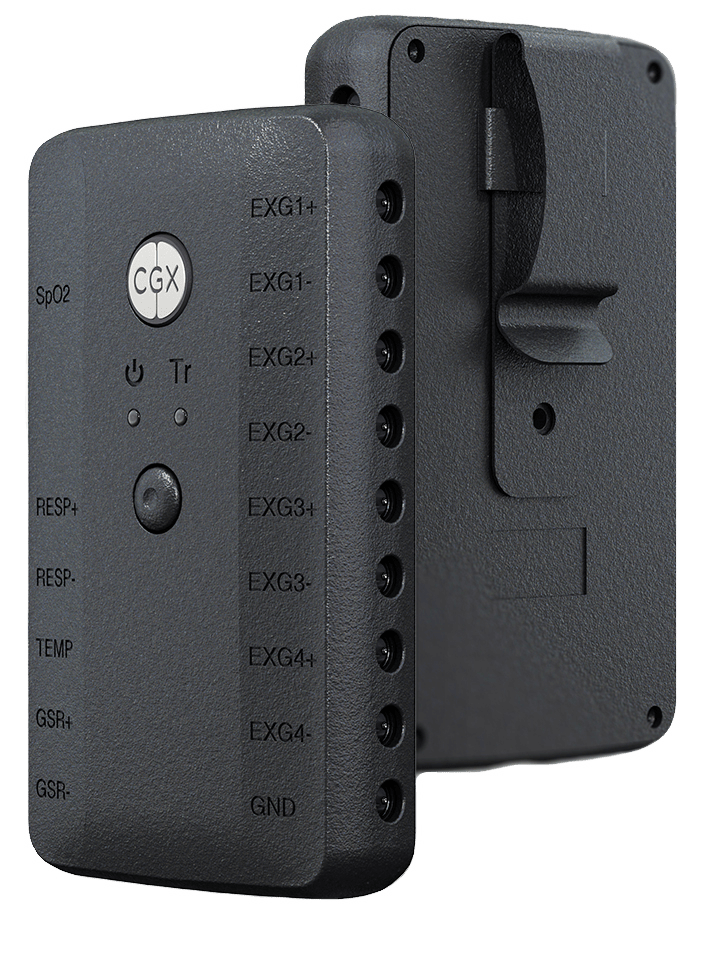
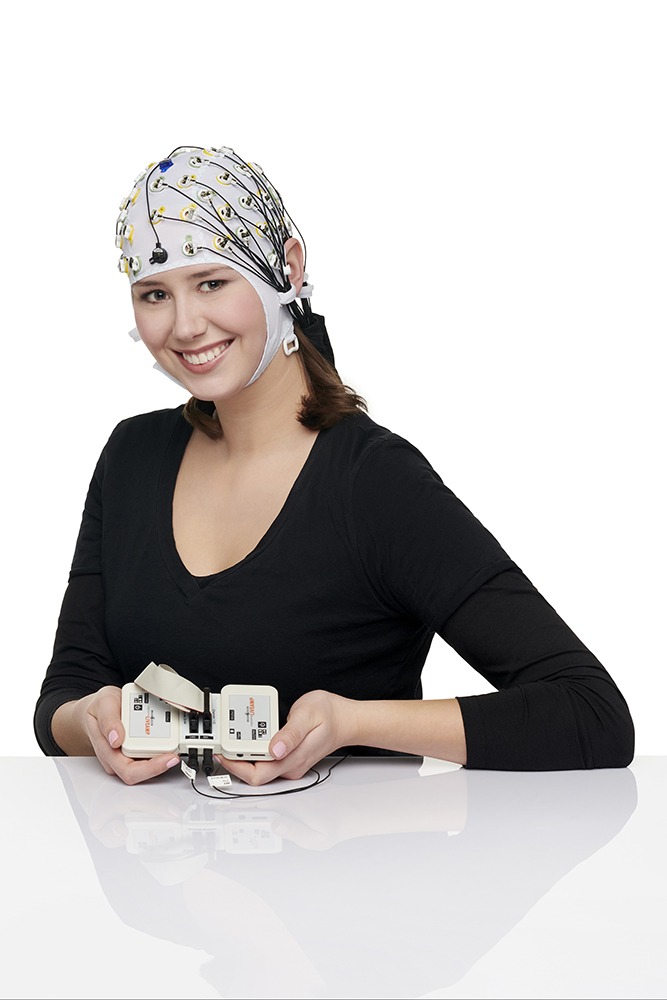
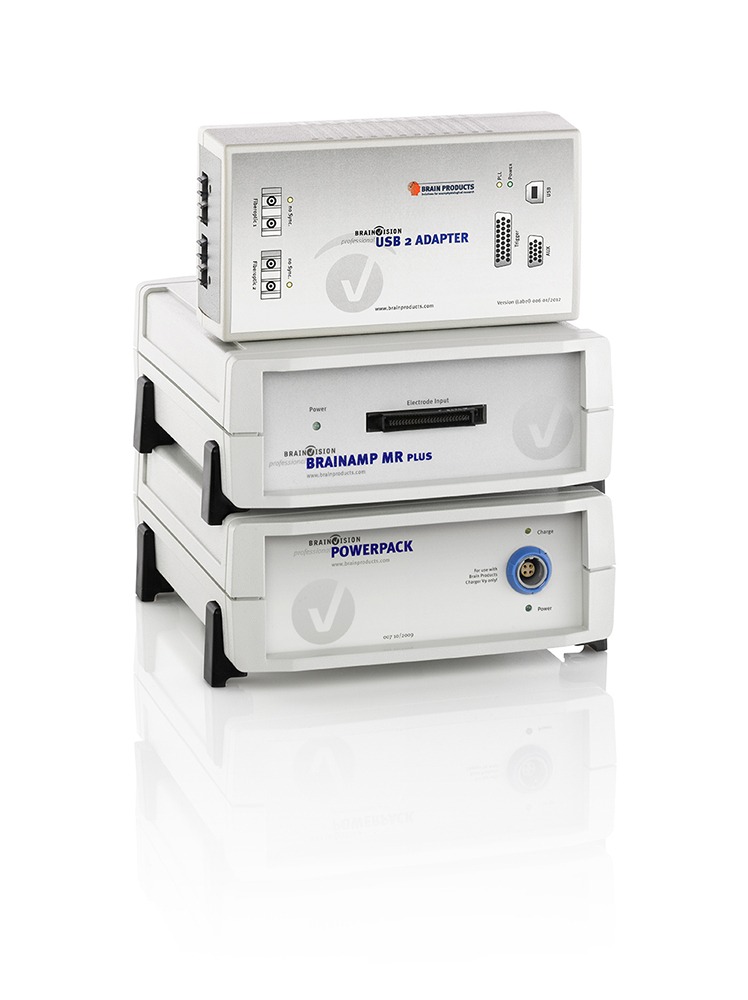
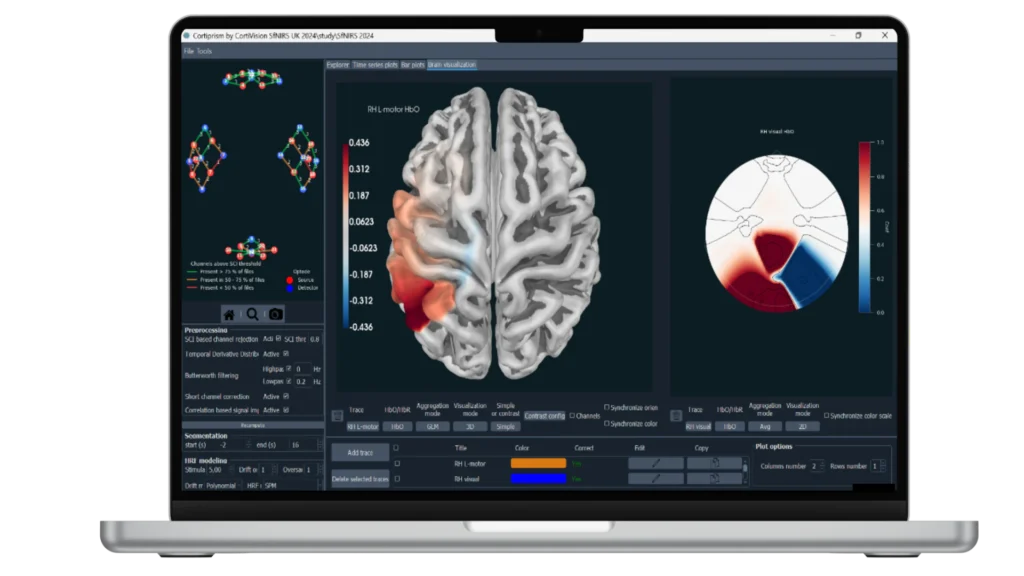
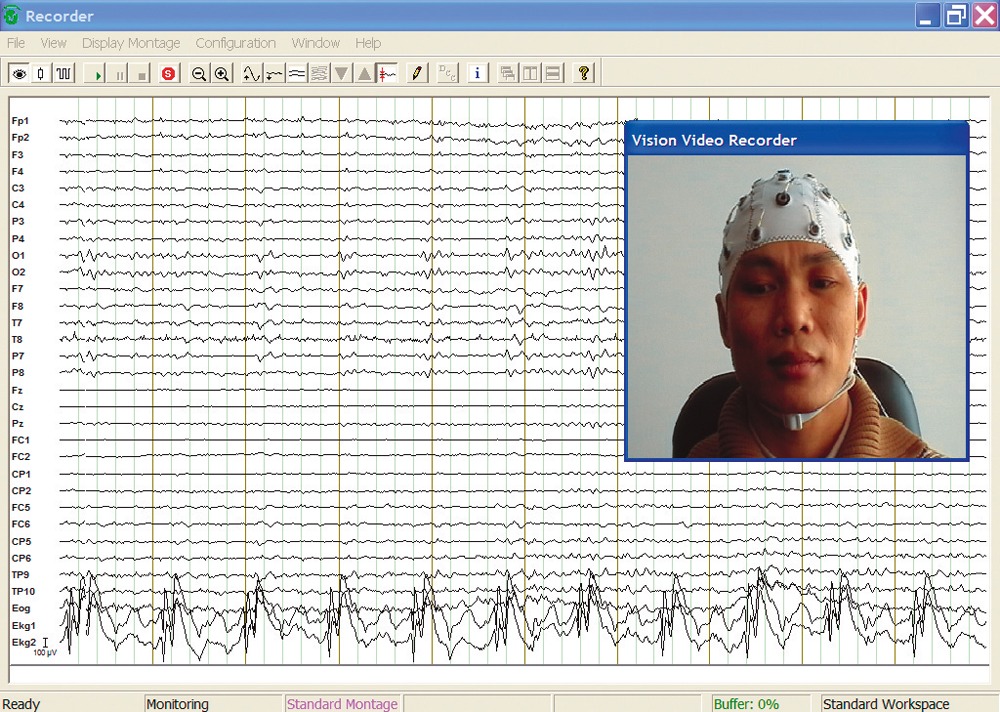
Functional near infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) uses different wavelengths of near infrared light to measure changes in blood oxygenation and deoxygenation (i.e., the hemodynamic response) across the cortex, which is often considered to be a correlate of brain activation. With fNIRS, specialized optodes are placed on the head, and their positions are secured in a grid-like fashion by caps or other headgear. Near infrared light is then emitted through one set of optodes and directed towards the scalp. Light that is not absorbed by the cortex is measured by surrounding detector optodes. This technique allows researchers to make inferences about brain activation without the need for magnetic fields or currents. Given its portability, fNIRS is versatile and can be used to answer a variety of questions about brain activation under more ecologically valid conditions (i.e., while participants are engaged in real-world activities). Similar to fMRI, it can also be combined with EEG; however, it is limited to cortical brain activation. Compared with EEG, fNIRS is a newer methodology and many labs previously developed homegrown solutions for measuring the hemodynamic response of the brain. We have partnered with leading fNIRS companies to offer cutting-edge, professional solutions that are backed by expert-level support.
fNIRS Related Products
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the penetration limit for fNIRS in tissue? / How deep can one probe with NIRS?
Light intensity is heavily attenuated in tissue and falls off exponentially from the illumination point. The maximum achievable probing depth of NIRS is limited by the illumination strength – determined by the thermal damaging threshold – and the detection sensitivity. Imaging depth strongly depends on the tissue type and the application. Typical achievable transmission limits of NIRS are about 12 cm for breast tissue, and 6 cm on the arm or leg. For brain imaging, the probing depth of NIRS is about 3 cm.
What is the achievable spatial resolution of NIRS?
Diffuse optical tomography is a low-resolution technique owing to the physics of light propagation in scattering media. Depending on the composition and size of the target tissue, the resolution is on the order of 5-10 mm.
What is the temporal resolution of NIRS?
The temporal resolution of an fNIRS device depends on its hardware as well as how its individual channels operate with respect to one another. Through time-multiplexing of the source firing, some systems can achieve anywhere between 3-25Hz depending on the optode montage. For a particular application, scan speed can be traded off against the desired coverage area (field-of-view) or source density (image resolution).
What types of scientific investigative studies is NIRS technology currently used in?
- Language, Cognition
- Learning, Memory
- Sensory, Motor, Visual
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Neurofeedback
- Acute Care, Ischemia
- Autism
- Animal Imaging: Rats
- Animal Imaging: Monkeys
- Child studies
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Studies
- Multimodal studies NIRS used simultaneously with EEG, TMS, eye-tracking, tDCS, and other modalities.
- Behavioral studies
- Motorcontrol & movement related studies
- Sports performance studies